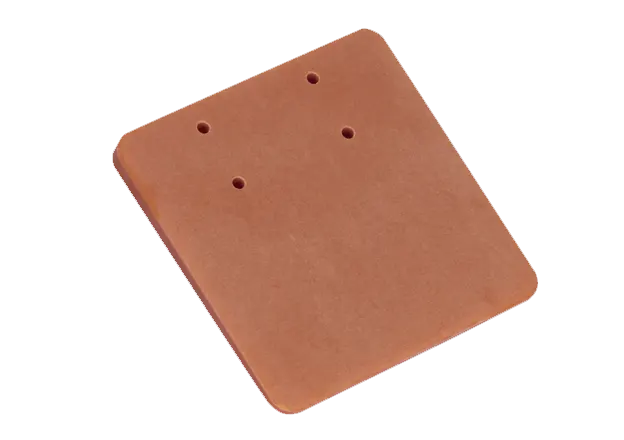
Bakelit, chemically known as phenolic plastic, is recognized as the first type of plastic to be industrially produced. It is renowned for its high mechanical strength, excellent insulation properties, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for manufacturing electrical materials such as switches, lamp heads, headphones, and telephone cases. The introduction of Bakelite has had a significant impact on industrial development.
Mechanical Properties
Phenolic plastic is characterized as a hard and brittle thermosetting material. Bakelite exhibits non-absorbent and non-conductive properties, along with high-temperature resistance and strength. Its malleability resembles that of wood, which is why it is often referred to as “Bakelite.” The production process involves mixing powdered phenolic resin with sawdust, asbestos, or clay, which is then pressed into molds at high temperatures to create finished products.
Bakelite features a hard surface that is brittle and fragile, producing a sound similar to wooden boards when struck. It is mostly opaque and comes in dark colors such as brown or black, and it does not soften in hot water. Its main component is phenolic resin, contributing to its insulating properties.
Molding Performance
Molding Properties: Bakelite has good molding properties, though it generally exhibits greater shrinkage and directionality compared to amino plastics. It may contain moisture volatiles, so preheating before molding is recommended. Additionally, the mold temperature and molding pressure should be increased if preheating is not performed.
Mold Temperature: The fluidity of Bakelite is significantly affected by mold temperature; typically, fluidity declines rapidly at temperatures above 160°C.
Hardening Speed: The hardening speed of Bakelite is generally slower than that of amino plastics, and the heat released during hardening is substantial. This can lead to high internal temperatures in large, thick-walled plastic parts, resulting in uneven hardening and potential overheating.
When the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol is less than 1, thermoplastic products can be obtained, known as thermoplastic phenolic resin or linear phenolic resin. This type does not undergo further condensation and can be cured by adding a curing agent, such as hexamethylenetetramine, at a curing temperature of 150°C, often mixed with fillers to create what is commonly known as Bakelite powder.
Conversely, when the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol exceeds 1, an alkali-catalyzed reaction produces stage A resin, which is a thermosetting phenolic resin soluble in organic solvents. This stage A resin contains hydroxymethyl groups that can undergo further condensation, eliminating the need for an external curing agent. Upon heating, this resin transforms into stage B resin, also known as semi-soluble phenolic resin, which is insoluble and non-melting but can swell and soften. Continued reaction leads to the formation of stage C resin, known as insoluble phenolic resin.
The curing of thermosetting phenolic resin can occur through two methods: room temperature curing and heat curing. Room temperature curing can utilize non-toxic agents like NL, although other options such as benzene sulfonyl chloride or petroleum sulfonic acid are available, albeit with higher toxicity and irritant properties.
Bestellvorgang
Q1: So senden Sie eine Verarbeitungsanfrage?A: Sie können uns über WhatsApp kontaktieren: +86 15323729231 oder E -Mail [email protected].B: Wir unterstützen die Dateiformate der Stufen-/Stl/IGES -Dateiformate. Sie können Ihre Dateien auch an unsere Service -E -Mail senden. Unser System generiert ein Angebot und eine Prozessempfehlungen innerhalb 1 Stunde.
Q2: Stellen Sie Entwurfsoptimierungsvorschläge an?A: Ja! Unser Engineering -Team bietet ein kostenloses DFM (Design für die Herstellung) Rezension, Bereitstellung von Optimierungsvorschlägen zur Verbesserung der Struktur und zur Reduzierung der Kosten.
Preisgestaltung & Lieferung
Q3: Was ist die minimale Bestellmenge (MOQ)?A: Kein MOQ! Wir akzeptieren Bestellungen aus 1 Stück, ob für 3D -Druck- oder CNC -Bearbeitung.
Q4: Was ist im Zitat enthalten?A: Das Angebot deckt die Materialkosten ab, Verarbeitungsgebühren, und grundlegende Oberflächenbehandlung (Z.B., Sandstrahlen). Zusätzliche Prozesse (Z.B., elektroplierend, Anodisierung) wird separat zitiert.
Q5: Was ist die Standardvorlaufzeit??
- CNC -Bearbeitung: 3-5 Tage (bis zu 7 Tage für komplexe Teile)
- 3D Druck: 72 Std.
Technologie & Qualität
Q6: Was ist die Bearbeitungsgenauigkeit??
- CNC -Bearbeitung: Schnelles Prototyping mit einer ± 0,05 mm -Toleranz, 0.1MM Form -Toleranz, und Oberflächenrauheit ra1.6 oder besser.
- 3D Druck:
- Harzteile: ± 0,2 mm
- Nylonteile: ± 0,3 mm
- Kunststoffteile: ± 0,3 mm
- Metallteile: ± 0,3 mm
Q7: Welche Materialien unterstützen Sie??✅ CNC -Bearbeitung:
- Aluminiumlegierung: 6061, 7075
- Kupferlegierung: Messing (H59), Rotkupfer (T2)
- Legierungsstahl: 45# Stahl
- Edelstahl: Sus304
- Kunststoff:
- ABS (Weiß, Schwarz)
- Pom (Weiß, Schwarz)
- Bakelit (Schwarz, Orange)
- Acryl (Transparent)
- FR4 Epoxy Board (Grün)
- PA6 Nylon (Weiß)
- Polycarbonat (Transparent)
✅ 3D -Druck:
- Harz, Nylon, Technische Kunststoffe, Edelstahl
After-Sales-Service
Q8: Was ist, wenn die Teile den Anforderungen nicht erfüllen??A: Wenn Mängel aufgrund unserer Verarbeitungsprobleme auftreten, Wir garantieren eine kostenlose Wiederaufbereitung.