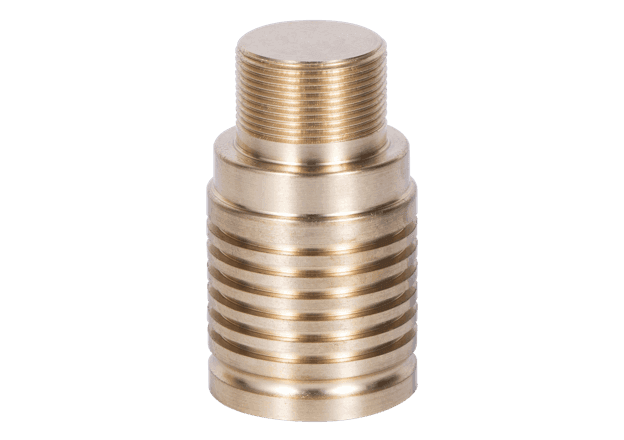
H59 brass is the most economical type of brass, known for its high strength, hardness, and good plasticity. It performs well under pressure processing, even in a hot state, and exhibits general corrosion resistance, with properties similar to H62.
Mechanical Properties
Tensile Strength (σb): ≥ 294 MPA
Elongation (δ10): ≥ 25%
Note: These tensile mechanical properties apply to plates with a thickness of 0.5 to 15 mm.
Microstructure
Room Temperature Structure: Ordinary brass is a copper-zinc binary alloy with varying zinc content, leading to different microstructures:
α Brass: Zinc content below 35%, consisting of a single-phase α solid solution.
(α + β) Messing: Zinc content between 36% and 46%, consisting of two phases (α and β).
β Brass: Zinc content above 46% to 50%, consisting solely of the β phase.
Pressure Processing Performance:
Alpha Single-Phase Brass (H96 to H65): Exhibits good plasticity and can withstand both hot and cold processing. However, it is prone to medium-temperature brittleness during hot processing (forging) at temperatures generally between 200°C and 700°C. To avoid brittleness, hot processing should occur above 700°C. The brittleness is attributed to the presence of ordered compounds (Cu3Zn and Cu9Zn) within the α-phase and low melting point eutectic films formed by trace elements like lead and bismuth.
Two-Phase Brass (H63 to H59): Contains both α-phase with good plasticity and a β-solid solution. The β-phase has high plasticity at elevated temperatures, while the β′-phase (ordered solid solution) is hard and brittle at lower temperatures. Thus, (α + β) brass should be forged in a hot state. Brass with more than 46% to 50% zinc (β brass) is hard and brittle and cannot be pressure processed.
Mechanical Properties Variation: The mechanical properties of brass vary with zinc content:
For α brass, both tensile strength (σb) and elongation (δ) increase with higher zinc content.
For (α + β) brass, room temperature strength increases with zinc content up to about 45%, beyond which strength decreases sharply due to the formation of the brittle r-phase (Cu5Zn8 compound). The plasticity of (α + β) brass decreases with increasing zinc content, making copper-zinc alloys with over 45% zinc impractical.
Anwendungen
Common brass is widely used in applications such as:
Water tank belts
Water supply and drainage pipes
Medallions
Bellows
Serpentine pipes
Condensation tubes
Shells
Various complex punching products
Small hardware
As zinc content increases from H63 to H59, these brasses can effectively withstand hot processing and are often used in machinery and electrical appliance parts, stamping parts, and musical instruments.
Heat Treatment
Hot Working Temperature: 730–820°C
Annealing Temperature: 600–670°C
Bestellvorgang
Q1: So senden Sie eine Verarbeitungsanfrage?A: Sie können uns über WhatsApp kontaktieren: +86 15323729231 oder E -Mail [email protected].B: Wir unterstützen die Dateiformate der Stufen-/Stl/IGES -Dateiformate. Sie können Ihre Dateien auch an unsere Service -E -Mail senden. Unser System generiert ein Angebot und eine Prozessempfehlungen innerhalb 1 Stunde.
Q2: Stellen Sie Entwurfsoptimierungsvorschläge an?A: Ja! Unser Engineering -Team bietet ein kostenloses DFM (Design für die Herstellung) Rezension, Bereitstellung von Optimierungsvorschlägen zur Verbesserung der Struktur und zur Reduzierung der Kosten.
Preisgestaltung & Lieferung
Q3: Was ist die minimale Bestellmenge (MOQ)?A: Kein MOQ! Wir akzeptieren Bestellungen aus 1 Stück, ob für 3D -Druck- oder CNC -Bearbeitung.
Q4: Was ist im Zitat enthalten?A: Das Angebot deckt die Materialkosten ab, Verarbeitungsgebühren, und grundlegende Oberflächenbehandlung (Z.B., Sandstrahlen). Zusätzliche Prozesse (Z.B., elektroplierend, Anodisierung) wird separat zitiert.
Q5: Was ist die Standardvorlaufzeit??
- CNC -Bearbeitung: 3-5 Tage (bis zu 7 Tage für komplexe Teile)
- 3D Druck: 72 Std.
Technologie & Qualität
Q6: Was ist die Bearbeitungsgenauigkeit??
- CNC -Bearbeitung: Schnelles Prototyping mit einer ± 0,05 mm -Toleranz, 0.1MM Form -Toleranz, und Oberflächenrauheit ra1.6 oder besser.
- 3D Druck:
- Harzteile: ± 0,2 mm
- Nylonteile: ± 0,3 mm
- Kunststoffteile: ± 0,3 mm
- Metallteile: ± 0,3 mm
Q7: Welche Materialien unterstützen Sie??✅ CNC -Bearbeitung:
- Aluminiumlegierung: 6061, 7075
- Kupferlegierung: Messing (H59), Rotkupfer (T2)
- Legierungsstahl: 45# Stahl
- Edelstahl: Sus304
- Kunststoff:
- ABS (Weiß, Schwarz)
- Pom (Weiß, Schwarz)
- Bakelit (Schwarz, Orange)
- Acryl (Transparent)
- FR4 Epoxy Board (Grün)
- PA6 Nylon (Weiß)
- Polycarbonat (Transparent)
✅ 3D -Druck:
- Harz, Nylon, Technische Kunststoffe, Edelstahl
After-Sales-Service
Q8: Was ist, wenn die Teile den Anforderungen nicht erfüllen??A: Wenn Mängel aufgrund unserer Verarbeitungsprobleme auftreten, Wir garantieren eine kostenlose Wiederaufbereitung.