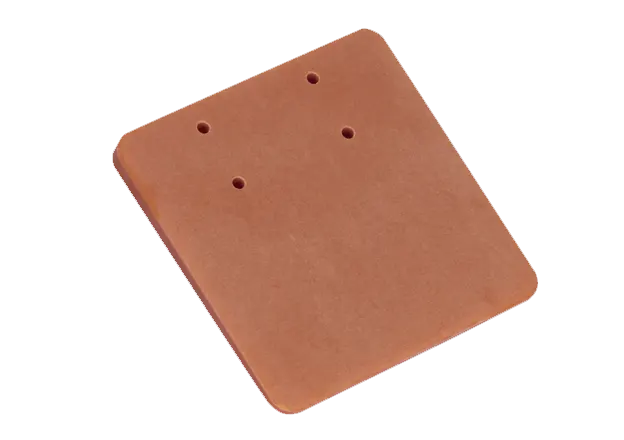
Bakelite, chemically known as phenolic plastic, is recognized as the first type of plastic to be industrially produced. It is renowned for its high mechanical strength, excellent insulation properties, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for manufacturing electrical materials such as switches, lamp heads, headphones, and telephone cases. The introduction of Bakelite has had a significant impact on industrial development.
Mechanical Properties
Phenolic plastic is characterized as a hard and brittle thermosetting material. Bakelite exhibits non-absorbent and non-conductive properties, along with high-temperature resistance and strength. Its malleability resembles that of wood, which is why it is often referred to as “Bakelite.” The production process involves mixing powdered phenolic resin with sawdust, asbestos, or clay, which is then pressed into molds at high temperatures to create finished products.
Bakelite features a hard surface that is brittle and fragile, producing a sound similar to wooden boards when struck. It is mostly opaque and comes in dark colors such as brown or black, and it does not soften in hot water. Its main component is phenolic resin, contributing to its insulating properties.
Molding Performance
Molding Properties: Bakelite has good molding properties, though it generally exhibits greater shrinkage and directionality compared to amino plastics. It may contain moisture volatiles, so preheating before molding is recommended. Additionally, the mold temperature and molding pressure should be increased if preheating is not performed.
Mold Temperature: The fluidity of Bakelite is significantly affected by mold temperature; typically, fluidity declines rapidly at temperatures above 160°C.
Hardening Speed: The hardening speed of Bakelite is generally slower than that of amino plastics, and the heat released during hardening is substantial. This can lead to high internal temperatures in large, thick-walled plastic parts, resulting in uneven hardening and potential overheating.
When the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol is less than 1, thermoplastic products can be obtained, known as thermoplastic phenolic resin or linear phenolic resin. This type does not undergo further condensation and can be cured by adding a curing agent, such as hexamethylenetetramine, at a curing temperature of 150°C, often mixed with fillers to create what is commonly known as Bakelite powder.
Conversely, when the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol exceeds 1, an alkali-catalyzed reaction produces stage A resin, which is a thermosetting phenolic resin soluble in organic solvents. This stage A resin contains hydroxymethyl groups that can undergo further condensation, eliminating the need for an external curing agent. Upon heating, this resin transforms into stage B resin, also known as semi-soluble phenolic resin, which is insoluble and non-melting but can swell and soften. Continued reaction leads to the formation of stage C resin, known as insoluble phenolic resin.
The curing of thermosetting phenolic resin can occur through two methods: room temperature curing and heat curing. Room temperature curing can utilize non-toxic agents like NL, although other options such as benzene sulfonyl chloride or petroleum sulfonic acid are available, albeit with higher toxicity and irritant properties.
Order Process
Q1: How to submit a processing request?A: You can contact us via WhatsApp: +86 15323729231 or email [email protected].B: We support STEP/STL/IGES file formats. You can also send your files to our service email. Our system will generate a quote and process recommendations within 1 hour.
Q2: Do you provide design optimization suggestions?A: Yes! Our engineering team offers a free DFM (Design for Manufacturability) review, providing optimization suggestions to improve structure and reduce costs.
Pricing & Delivery
Q3: What is the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)?A: No MOQ! We accept orders starting from 1 piece, whether for 3D printing or CNC machining.
Q4: What is included in the quotation?A: The quote covers material costs, processing fees, and basic surface treatment (e.g., sandblasting). Additional processes (e.g., electroplating, anodizing) will be quoted separately.
Q5: What is the standard lead time?
- CNC Machining: 3-5 days (up to 7 days for complex parts)
- 3D Printing: 72 hours
Technology & Quality
Q6: What is the machining accuracy?
- CNC Machining: Fast prototyping with a ±0.05mm tolerance, 0.1mm form tolerance, and surface roughness Ra1.6 or better.
- 3D Printing:
- Resin parts: ±0.2mm
- Nylon parts: ±0.3mm
- Plastic parts: ±0.3mm
- Metal parts: ±0.3mm
Q7: What materials do you support?✅ CNC Machining:
- Aluminum Alloy: 6061, 7075
- Copper Alloy: Brass (H59), Red Copper (T2)
- Alloy Steel: 45# Steel
- Stainless Steel: SUS304
- Plastics:
- ABS (White, Black)
- POM (White, Black)
- Bakelite (Black, Orange)
- Acrylic (Transparent)
- FR4 Epoxy Board (Green)
- PA6 Nylon (White)
- Polycarbonate (Transparent)
✅ 3D Printing:
- Resin, Nylon, Engineering Plastics, Stainless Steel
After-Sales Service
Q8: What if the parts do not meet the requirements?A: If defects occur due to our processing issues, we guarantee free remanufacturing.