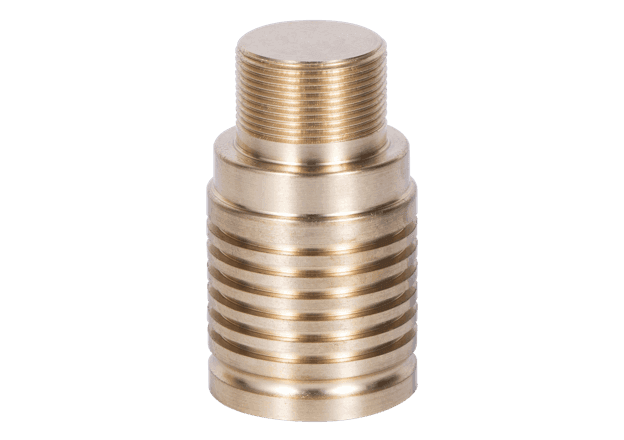
H59 brass is the most economical type of brass, known for its high strength, hardness, and good plasticity. It performs well under pressure processing, even in a hot state, and exhibits general corrosion resistance, with properties similar to H62.
Mechanical Properties
Tensile Strength (σb): ≥ 294 MPa
Elongation (δ10): ≥ 25%
Note: These tensile mechanical properties apply to plates with a thickness of 0.5 to 15 mm.
Microstructure
Room Temperature Structure: Ordinary brass is a copper-zinc binary alloy with varying zinc content, leading to different microstructures:
α Brass: Zinc content below 35%, consisting of a single-phase α solid solution.
(α + β) Brass: Zinc content between 36% and 46%, consisting of two phases (α and β).
β Brass: Zinc content above 46% to 50%, consisting solely of the β phase.
Pressure Processing Performance:
Alpha Single-Phase Brass (H96 to H65): Exhibits good plasticity and can withstand both hot and cold processing. However, it is prone to medium-temperature brittleness during hot processing (forging) at temperatures generally between 200°C and 700°C. To avoid brittleness, hot processing should occur above 700°C. The brittleness is attributed to the presence of ordered compounds (Cu3Zn and Cu9Zn) within the α-phase and low melting point eutectic films formed by trace elements like lead and bismuth.
Two-Phase Brass (H63 to H59): Contains both α-phase with good plasticity and a β-solid solution. The β-phase has high plasticity at elevated temperatures, while the β′-phase (ordered solid solution) is hard and brittle at lower temperatures. Thus, (α + β) brass should be forged in a hot state. Brass with more than 46% to 50% zinc (β brass) is hard and brittle and cannot be pressure processed.
Mechanical Properties Variation: The mechanical properties of brass vary with zinc content:
For α brass, both tensile strength (σb) and elongation (δ) increase with higher zinc content.
For (α + β) brass, room temperature strength increases with zinc content up to about 45%, beyond which strength decreases sharply due to the formation of the brittle r-phase (Cu5Zn8 compound). The plasticity of (α + β) brass decreases with increasing zinc content, making copper-zinc alloys with over 45% zinc impractical.
Applications
Common brass is widely used in applications such as:
Water tank belts
Water supply and drainage pipes
Medallions
Bellows
Serpentine pipes
Condensation tubes
Shells
Various complex punching products
Small hardware
As zinc content increases from H63 to H59, these brasses can effectively withstand hot processing and are often used in machinery and electrical appliance parts, stamping parts, and musical instruments.
Heat Treatment
Hot Working Temperature: 730–820°C
Annealing Temperature: 600–670°C
Order Process
Q1: How to submit a processing request?A: You can contact us via WhatsApp: +86 15323729231 or email [email protected].B: We support STEP/STL/IGES file formats. You can also send your files to our service email. Our system will generate a quote and process recommendations within 1 hour.
Q2: Do you provide design optimization suggestions?A: Yes! Our engineering team offers a free DFM (Design for Manufacturability) review, providing optimization suggestions to improve structure and reduce costs.
Pricing & Delivery
Q3: What is the Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)?A: No MOQ! We accept orders starting from 1 piece, whether for 3D printing or CNC machining.
Q4: What is included in the quotation?A: The quote covers material costs, processing fees, and basic surface treatment (e.g., sandblasting). Additional processes (e.g., electroplating, anodizing) will be quoted separately.
Q5: What is the standard lead time?
- CNC Machining: 3-5 days (up to 7 days for complex parts)
- 3D Printing: 72 hours
Technology & Quality
Q6: What is the machining accuracy?
- CNC Machining: Fast prototyping with a ±0.05mm tolerance, 0.1mm form tolerance, and surface roughness Ra1.6 or better.
- 3D Printing:
- Resin parts: ±0.2mm
- Nylon parts: ±0.3mm
- Plastic parts: ±0.3mm
- Metal parts: ±0.3mm
Q7: What materials do you support?✅ CNC Machining:
- Aluminum Alloy: 6061, 7075
- Copper Alloy: Brass (H59), Red Copper (T2)
- Alloy Steel: 45# Steel
- Stainless Steel: SUS304
- Plastics:
- ABS (White, Black)
- POM (White, Black)
- Bakelite (Black, Orange)
- Acrylic (Transparent)
- FR4 Epoxy Board (Green)
- PA6 Nylon (White)
- Polycarbonate (Transparent)
✅ 3D Printing:
- Resin, Nylon, Engineering Plastics, Stainless Steel
After-Sales Service
Q8: What if the parts do not meet the requirements?A: If defects occur due to our processing issues, we guarantee free remanufacturing.